
This combination is pronounced /mb/, not /mp/.ġ1. πέμπω Be careful with the combination μπ. The pronunciation should be theh- Os, not th Eh-os.ġ0. θεός The little slanted line above the ο indicates that this vowel should be pronounced slightly louder than the one before it. Your instructor may ask you to pronounce these words in class.ĩ. If you are studying in a classroom setting, listen to your instructor's pronunciation, and attempt to imitate it. Practice pronouncing the following words. They only designate the way the vowels function with regard to the placement of accent marks, which we will learn in the lesson on diacritics.

The terms long and short do not indicate anything about the pronunciation of the Greek vowels in this course. By the middle of the Hellenistic period, though, this distinction was not consistently made. In the Classical period (before 350 BCE), long vowels wereĪctually pronounced for a longer time than short vowels, about twice as long. The other three vowels (α, ι, υ) may be considered either short or long, depending upon the context in which they occur. In printed editions of texts from the Hellenistic period, upper case letters are used for proper names and at theīeginning of a paragraph, not at the beginning of every sentence.įor purposes of accentuation (the placement of accent marks) the Greek vowels are divided into three groups. Usage of the Upper Case in Printed Greek Texts Be careful to distinguish Η and Υįrom the English letters that resemble them. You should concentrate on the following upper case

Two of these (Ρ, and Χ) should be carefully distinguished from the English letters that look like them. Others resemble their lower case Greek equivalents: Θ, Π, Ρ, Φ, Χ, Ψ. Several of the upper case letters resemble their English equivalents: Α, Β, Ε, Ζ, Ι, Κ, Μ, Ν, Ο, Τ. y/ like German ü, or sometimes / u/ as in r ule or even / ʊ/ as in h ook Unaspirated / t/ as in s top (but unlike top) r/ more like the Spanish trilled r than English r.Ī trilled / r/ like Spanish r, not like English rīut z as in zoo before beta (β), gamma (γ), delta (δ), and mu (μ) i/ as in “mach ine” (long) or /ɪ/ as in “f it” (short) θ/ as in “ thin” but not /ð/ as in “ then” θ/ as in “ thin” but not /ð/ as in “ then” (Contrast δ above.)
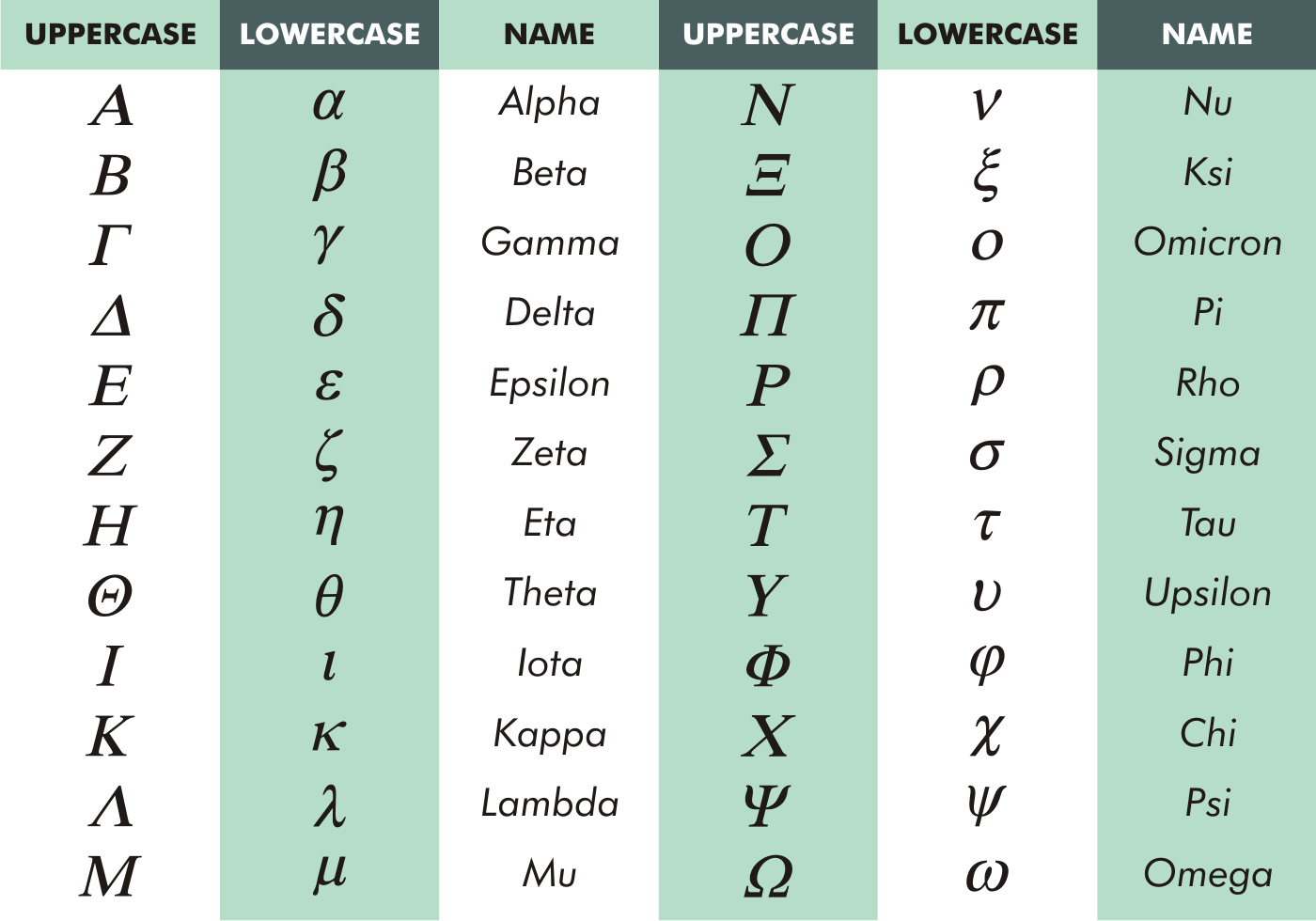
e/ like the first part of the a in l ate ð/ (th) as in “ then” but not /θ/ as in “ thin” (Contrast Θ θ below.) ð/ (th) as in “ then” but not /θ/ as in “thin” (Contrast Θ θ below.)

Softer than the g in " get", more like Spanish g in la go g/ as in “ go” but /y/ as in “ yet” before /i/ or /e/ sounds V as in " vote" (but more like Spanish b/v in vaca and bote) a:/ as in “f ather” or sometimes / æ/ as c at The Upper Case Greek Letters, Their Names and Pronunciation


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
